Transports¶
Transports define how MCP clients and servers communicate. MCP supports two primary transport mechanisms.
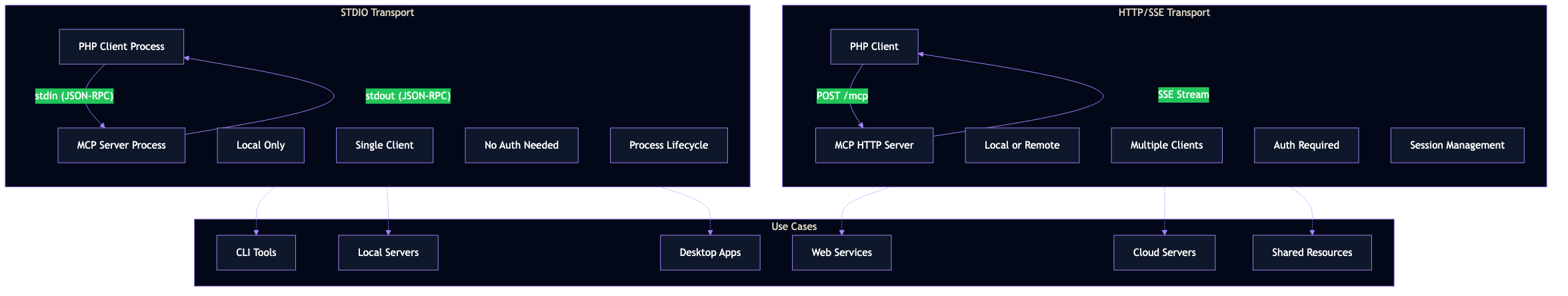
Overview¶
| Transport | Use Case | Latency | Setup Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| stdio | Local processes | Low | Simple |
| HTTP/SSE | Remote servers | Medium | Moderate |
stdio Transport¶
The stdio (standard input/output) transport runs the MCP server as a subprocess, communicating via standard streams.
How It Works¶
graph LR
subgraph Client["PHP Client Process"]
C[MCP Client]
Write[Write to stdin]
Read[Read from stdout]
end
subgraph Server["Server Process"]
S[MCP Server]
In[Read stdin]
Out[Write stdout]
end
C --> Write
Write -->|JSON-RPC| In
In --> S
S --> Out
Out -->|JSON-RPC| Read
Read --> C
PHP Implementation¶
<?php
use Symfony\Component\Process\Process;
class StdioTransport
{
private Process $process;
private $stdin;
private $stdout;
public function __construct(
private string $command,
private array $args = [],
private array $env = []
) {}
public function connect(): void
{
$fullCommand = array_merge([$this->command], $this->args);
$this->process = new Process($fullCommand);
$this->process->setEnv(array_merge($_ENV, $this->env));
$this->process->setTimeout(null);
$this->process->start();
// Get streams
$this->stdin = $this->process->getInput();
$this->stdout = $this->process->getOutput();
}
public function send(array $message): void
{
$json = json_encode($message) . "\n";
fwrite($this->stdin, $json);
fflush($this->stdin);
}
public function receive(): ?array
{
$line = fgets($this->stdout);
if ($line === false) {
return null;
}
return json_decode(trim($line), true);
}
public function close(): void
{
$this->process->stop(3);
}
}
Configuration Example¶
$config = [
'transport' => 'stdio',
'command' => 'npx',
'args' => ['-y', '@notionhq/notion-mcp-server'],
'env' => [
'NOTION_TOKEN' => env('NOTION_TOKEN'),
],
];
Advantages¶
- Simple setup - Just start a process
- Low latency - Direct pipe communication
- Secure - No network exposure
- Self-contained - Server lifecycle tied to client
Limitations¶
- Single client - One client per server process
- Local only - Cannot run on remote machines
- Process management - Must handle crashes/restarts
HTTP/SSE Transport¶
The Streamable HTTP transport enables remote communication using HTTP POST for requests and Server-Sent Events (SSE) for notifications.
How It Works¶
sequenceDiagram
participant C as PHP Client
participant S as MCP HTTP Server
Note over C,S: Session Initialization
C->>S: POST /mcp (initialize)
S-->>C: 200 OK + Mcp-Session-Id header
Note over C,S: Response includes session ID
Note over C,S: Tool Execution
C->>S: POST /mcp (tools/call)
Note over C: Include Mcp-Session-Id header
S-->>C: 200 OK + result
Note over C,S: Event Stream (Optional)
C->>S: GET /mcp
S-->>C: SSE stream
Note over C: Receive notifications
PHP Implementation¶
<?php
use GuzzleHttp\Client;
use GuzzleHttp\Psr7\Request;
class HttpTransport
{
private Client $client;
private ?string $sessionId = null;
private ?string $eventStreamUrl = null;
public function __construct(
private string $baseUrl,
private array $headers = []
) {
$this->client = new Client([
'base_uri' => $this->baseUrl,
'timeout' => 30,
]);
}
public function connect(): void
{
// Initial request to establish session
$response = $this->send([
'jsonrpc' => '2.0',
'id' => 1,
'method' => 'initialize',
'params' => [
'protocolVersion' => '2024-11-05',
'capabilities' => [],
'clientInfo' => [
'name' => 'rea-mcp-client',
'version' => '1.0.0',
],
],
]);
// Extract session ID from response headers
$this->sessionId = $response->getHeader('Mcp-Session-Id')[0] ?? null;
}
public function send(array $message): array
{
$headers = array_merge($this->headers, [
'Content-Type' => 'application/json',
]);
if ($this->sessionId !== null) {
$headers['Mcp-Session-Id'] = $this->sessionId;
}
$response = $this->client->post('/mcp', [
'headers' => $headers,
'json' => $message,
]);
return json_decode($response->getBody()->getContents(), true);
}
public function openEventStream(callable $onMessage): void
{
$headers = [
'Accept' => 'text/event-stream',
'Mcp-Session-Id' => $this->sessionId,
];
$response = $this->client->get('/mcp', [
'headers' => $headers,
'stream' => true,
]);
$body = $response->getBody();
while (!$body->eof()) {
$line = $body->read(1024);
if (str_starts_with($line, 'data: ')) {
$data = json_decode(substr($line, 6), true);
$onMessage($data);
}
}
}
public function close(): void
{
if ($this->sessionId !== null) {
$this->client->delete('/mcp', [
'headers' => ['Mcp-Session-Id' => $this->sessionId],
]);
}
}
}
Configuration Example¶
$config = [
'transport' => 'http',
'url' => 'https://mcp.example.com',
'headers' => [
'Authorization' => 'Bearer ' . env('MCP_AUTH_TOKEN'),
],
'timeout' => 30,
];
HTTP Endpoints¶
| Endpoint | Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
/mcp |
POST | Send JSON-RPC requests |
/mcp |
GET | Open SSE stream for notifications |
/mcp |
DELETE | Close session |
/health |
GET | Health check (no auth required) |
Headers¶
| Header | Direction | Description |
|---|---|---|
Mcp-Session-Id |
Both | Session identifier |
Mcp-Protocol-Version |
Request | Protocol version |
Last-Event-ID |
Request | Resume SSE from event |
Advantages¶
- Remote access - Connect to servers anywhere
- Multi-client - Multiple clients per server
- Scalable - Standard HTTP infrastructure
- Resumable - SSE supports reconnection
Limitations¶
- Authentication required - Must implement auth
- Network latency - Higher than stdio
- Session management - Must handle sessions
Choosing a Transport¶
Use stdio When¶
- Server runs on the same machine
- Single client connection is sufficient
- You want simple deployment
- Security is paramount (no network exposure)
Use HTTP When¶
- Server needs to run remotely
- Multiple clients need simultaneous access
- You need to scale horizontally
- Building a shared service
Security Considerations¶
stdio Security¶
// Ensure no debug output on stdout
ini_set('display_errors', '0');
error_reporting(0);
// Redirect errors to stderr
ini_set('error_log', 'php://stderr');
HTTP Security¶
// Validate origin header
$origin = $request->getHeader('Origin')[0] ?? '';
if (!in_array($origin, $allowedOrigins)) {
return new Response(403, [], 'Forbidden');
}
// Require authentication
if (!$this->validateAuthToken($request)) {
return new Response(401, [], 'Unauthorized');
}
// Rate limiting
if ($this->rateLimiter->tooManyAttempts($clientId)) {
return new Response(429, [], 'Rate limited');
}
Message Flow¶
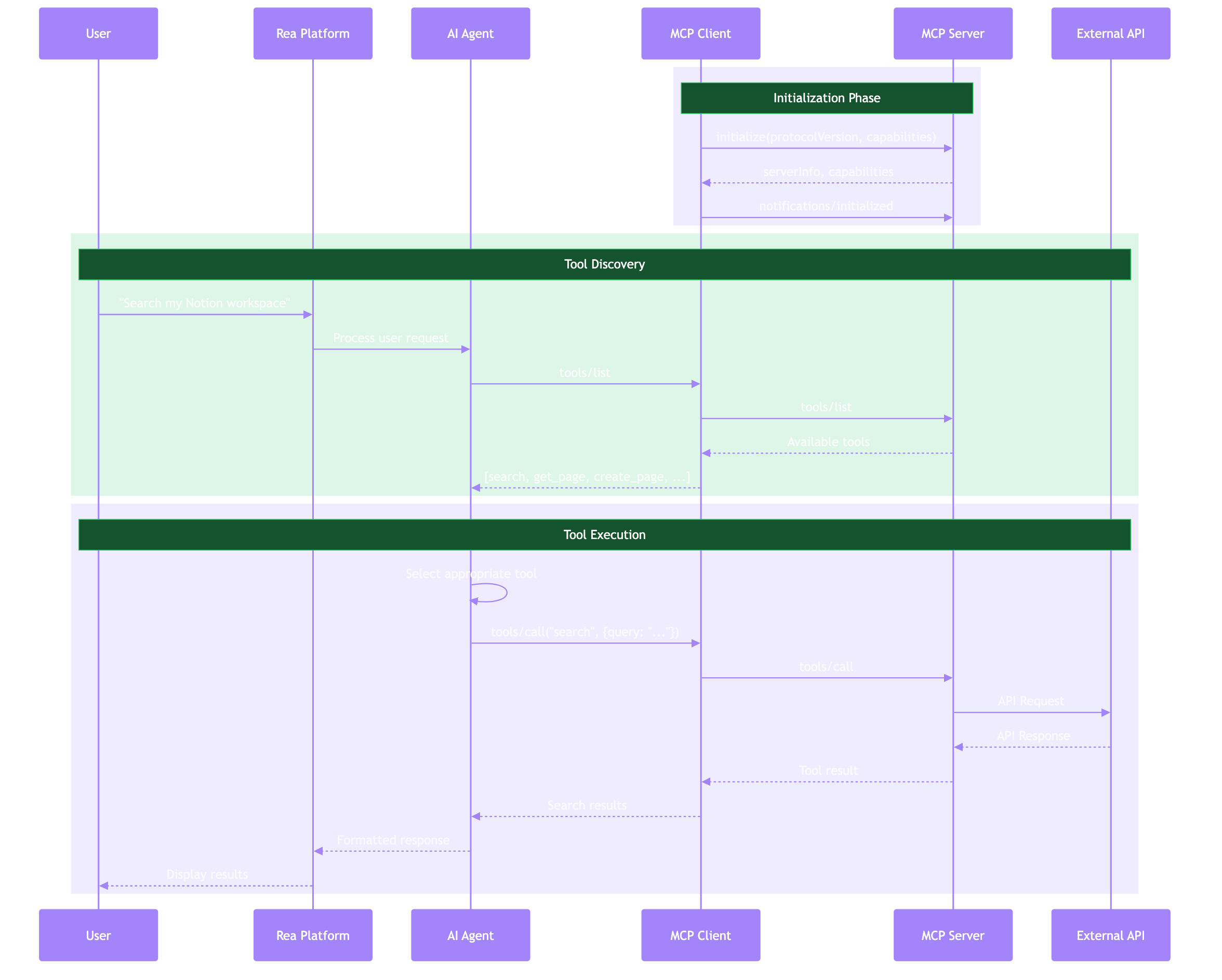
JSON-RPC Format¶
All messages follow JSON-RPC 2.0:
Request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {
"name": "search",
"arguments": {"query": "test"}
}
}
Response:
Notification (no id):
Next Steps¶
- PHP Client Implementation - Build a complete client
- PHP Server Implementation - Build your own server
- Security Reference - Secure your transports