MCP Architecture Overview¶
This document provides a detailed technical overview of the Model Context Protocol architecture and how it applies to Rea.
Core Architecture¶
MCP follows a client-server architecture with three main participants:
graph TB
subgraph Host["Host (Rea Platform)"]
UI[User Interface]
Agent[AI Agent]
Client1[MCP Client 1]
Client2[MCP Client 2]
Client3[MCP Client N]
end
subgraph Servers["MCP Servers"]
Server1[Notion Server]
Server2[Slack Server]
Server3[Custom Server]
end
UI --> Agent
Agent --> Client1
Agent --> Client2
Agent --> Client3
Client1 --> Server1
Client2 --> Server2
Client3 --> Server3
Component Roles¶
Host (Rea Platform)¶
The host is the main AI application responsible for:
- Managing the user experience
- Coordinating between AI agents and MCP clients
- Aggregating capabilities from multiple servers
- Enforcing security policies
- Handling user consent for operations
MCP Client¶
Each MCP client maintains a 1:1 connection with an MCP server:
- Establishes and maintains server connection
- Handles protocol negotiation and capability exchange
- Routes requests to the appropriate server
- Manages session state
MCP Server¶
Servers expose capabilities to clients:
- Declares available tools, resources, and prompts
- Executes tool calls and returns results
- Provides resource content on request
- Can run locally (stdio) or remotely (HTTP)
Protocol Layers¶
MCP has two distinct layers:
Data Layer (Protocol)¶
The inner layer defines the message format and semantics:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {
"name": "search_notion",
"arguments": {
"query": "meeting notes"
}
}
}
Components:
- JSON-RPC 2.0 message format
- Lifecycle management (initialize, shutdown)
- Capability negotiation
- Request/response patterns
- Notifications
Transport Layer¶
The outer layer handles communication:
stdio Transport¶
For local process communication:
- Server runs as subprocess of client
- Messages sent via standard I/O
- Simple, secure, no network exposure
- Used by Claude Desktop, VS Code, etc.
Streamable HTTP Transport¶
For remote server communication:
- RESTful endpoints for requests
- Server-Sent Events for real-time updates
- Session management via headers
- Supports multiple concurrent clients
Message Flow¶
Initialization Sequence¶
sequenceDiagram
participant C as Client
participant S as Server
C->>S: initialize(protocolVersion, capabilities, clientInfo)
S-->>C: {protocolVersion, capabilities, serverInfo}
C->>S: notifications/initialized
Note over C,S: Connection established
Tool Discovery and Execution¶
sequenceDiagram
participant H as Host
participant C as Client
participant S as Server
H->>C: List available tools
C->>S: tools/list
S-->>C: {tools: [...]}
C-->>H: Tool definitions
H->>C: Execute "search_notion"
C->>S: tools/call(name, arguments)
S-->>C: {content: [...]}
C-->>H: Tool result
Capability Negotiation¶
During initialization, both parties declare their capabilities:
Server Capabilities¶
{
"capabilities": {
"tools": {
"listChanged": true
},
"resources": {
"subscribe": true,
"listChanged": true
},
"prompts": {
"listChanged": true
},
"logging": {}
}
}
Client Capabilities¶
Rea-Specific Architecture¶
Rea.pro is an agentic framework and orchestration platform that uses LLaMA with Reflection prompts for enhanced reasoning. MCP integration extends Rea's capabilities to connect with external services and expose Rea's features to other AI applications.
LLaMA + MCP Integration¶
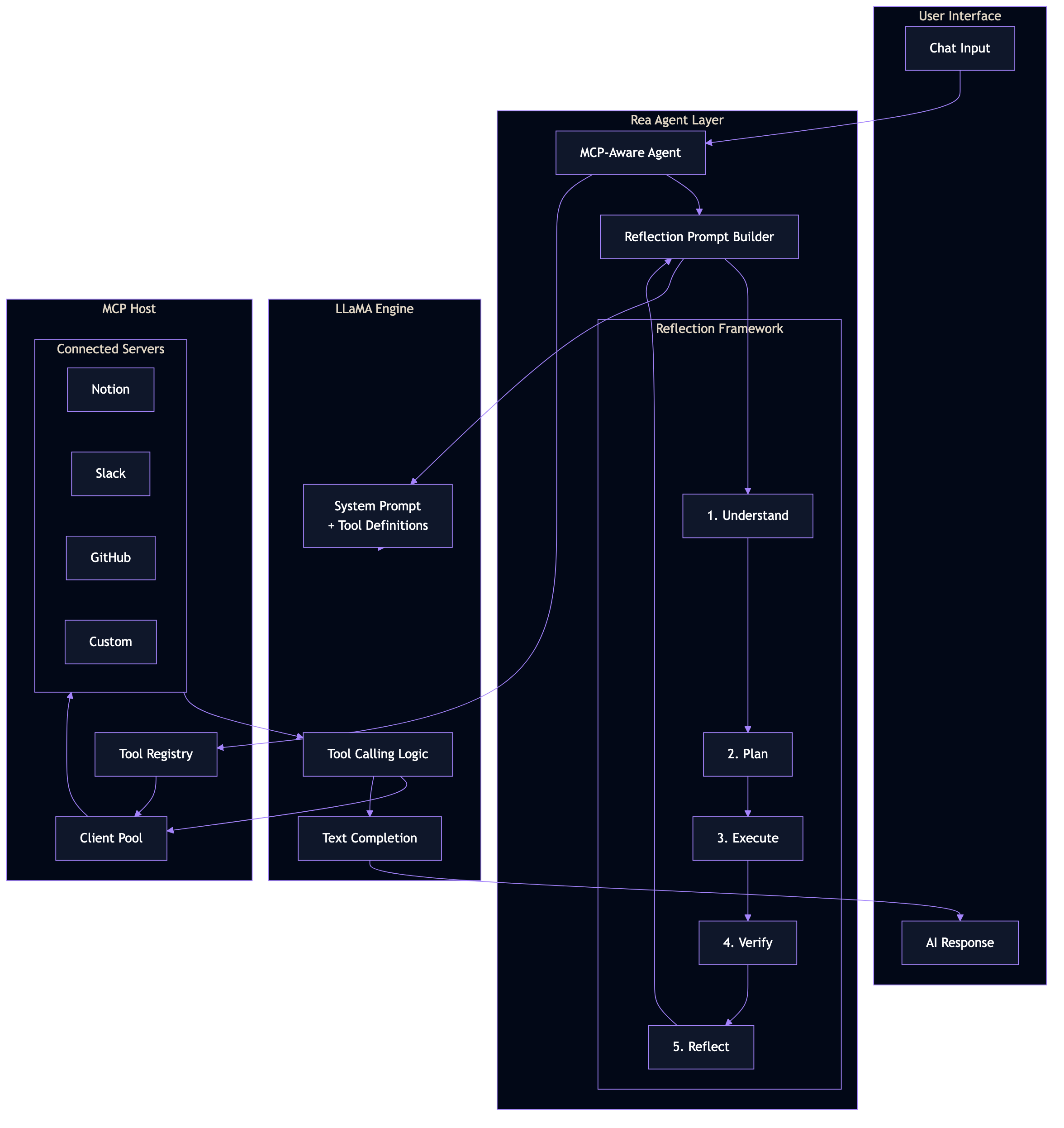
The integration layer bridges LLaMA's tool calling with MCP's standardized protocol:
- MCP-Aware Agent receives user queries and available tools
- Reflection Prompt Builder constructs system prompts with the 5-step framework
- LLaMA processes the prompt, deciding when to call MCP tools
- MCP Host routes tool calls to the appropriate connected servers
- Results flow back through the agent for final response generation
Dual MCP Architecture¶
Rea implements MCP in two directions:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ REA.PRO │
│ │
┌─────────────┐ │ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────────────┐ │ ┌──────────────┐
│ Notion │◄────┼──┤ MCP HOST │ │ MCP SERVER │───┼────►│ Claude │
│ Slack │ │ │ (Client) │ │ (Exposes Rea) │ │ │ Desktop │
│ GitHub │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ Custom │ │ │ Consumes │ │ Provides: │ │ │ Cursor │
└─────────────┘ │ │ external │ │ - Consulting Pods │ │ │ │
│ │ MCP tools │ │ - Command Room │ │ │ Other MCP │
│ └──────┬───────┘ │ - n8n Workflows │ │ │ Clients │
│ │ └──────────┬───────────┘ │ └──────────────┘
│ │ │ │
│ ▼ ▼ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ LLaMA + Reflection │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ System Prompt + Tool Definitions + Context │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Consulting Pods via MCP¶

Rea's Consulting Pods (multi-agent workflows) are exposed as MCP tools, allowing external clients to:
- Create new consulting pods for complex tasks
- Execute existing pods with custom inputs
- Query pod results and execution history
Command Room Integration¶
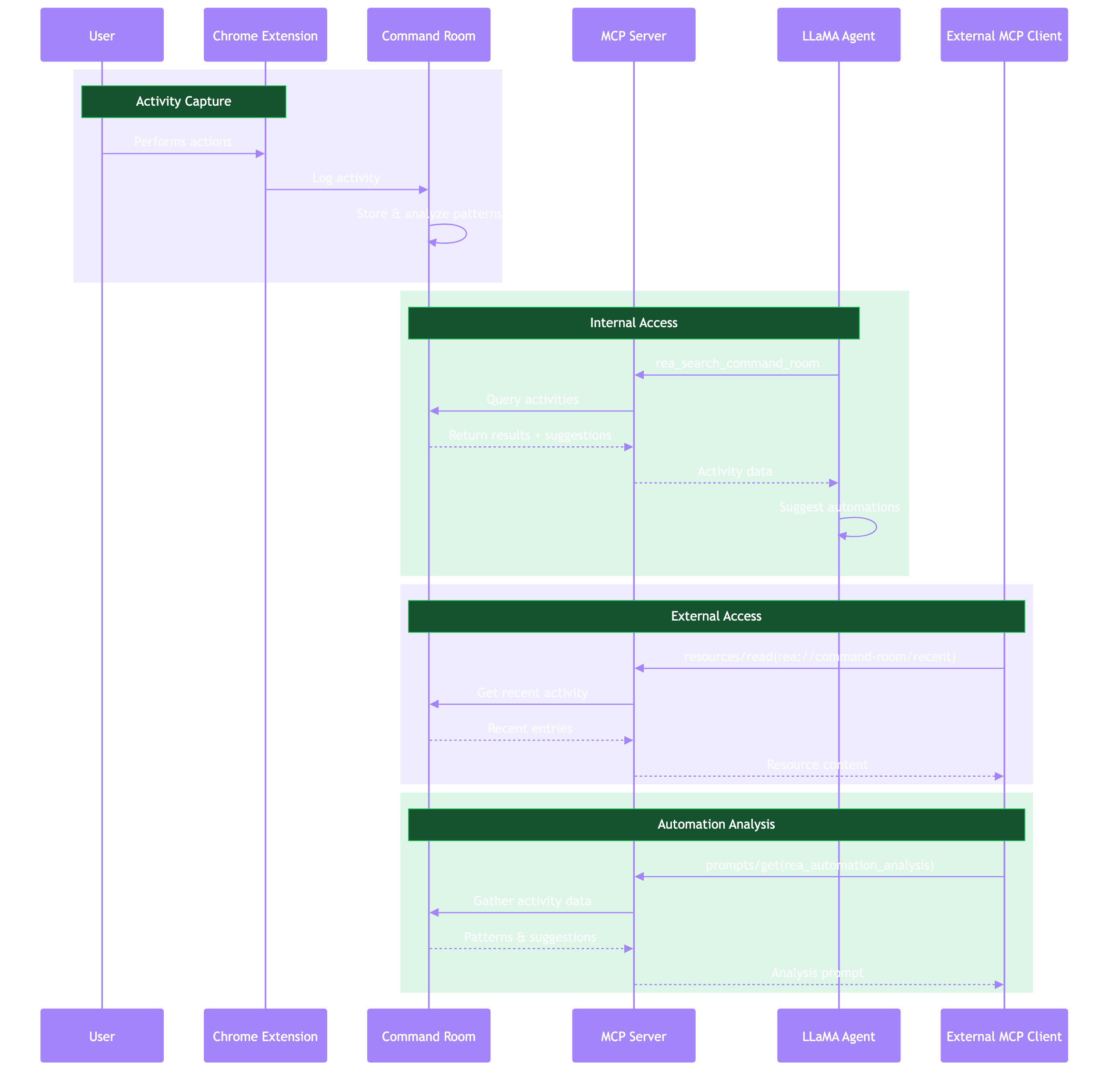
The Command Room captures user activity via browser extension and provides:
- Resources: Recent activity data accessible via
rea://command-room/recent - Tools:
rea_search_command_roomfor querying historical activities - Prompts:
rea_automation_analysisfor suggesting automations based on patterns
Proposed Rea MCP Architecture¶
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Rea Platform (Laravel) │
│ │
│ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ API │───►│ Agent │───►│ Reflection Prompt │ │
│ │ Controller │ │ Service │ │ Builder │ │
│ └─────────────┘ └──────┬──────┘ └─────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ▼ │
│ ┌────────────────┐ │
│ │ MCP Manager │ │
│ │ Service │ │
│ └───────┬────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ┌─────────────────┼─────────────────┐ │
│ ▼ ▼ ▼ │
│ ┌────────────┐ ┌────────────┐ ┌────────────┐ │
│ │ Stdio │ │ HTTP │ │ Custom │ │
│ │ Client │ │ Client │ │ Client │ │
│ └─────┬──────┘ └─────┬──────┘ └─────┬──────┘ │
└────────┼─────────────────┼─────────────────┼────────────────────────┘
│ │ │
▼ ▼ ▼
┌────────────┐ ┌────────────┐ ┌────────────┐
│ Local │ │ Remote │ │ Remote │
│ Server │ │ Server │ │ Server │
│ (stdio) │ │ (HTTP) │ │ (HTTP) │
└────────────┘ └────────────┘ └────────────┘
Key Components¶
MCP Manager Service¶
Central service managing all MCP connections:
class MCPManagerService
{
private array $clients = [];
public function registerServer(string $name, ServerConfig $config): void
{
$client = $this->createClient($config);
$client->initialize();
$this->clients[$name] = $client;
}
public function getTools(): array
{
$tools = [];
foreach ($this->clients as $name => $client) {
$serverTools = $client->listTools();
foreach ($serverTools as $tool) {
$tools["{$name}.{$tool['name']}"] = $tool;
}
}
return $tools;
}
public function callTool(string $fullName, array $arguments): mixed
{
[$serverName, $toolName] = explode('.', $fullName, 2);
return $this->clients[$serverName]->callTool($toolName, $arguments);
}
}
Server Configuration¶
class ServerConfig
{
public function __construct(
public string $name,
public TransportType $transport,
public ?string $command = null, // For stdio
public ?array $args = null, // For stdio
public ?string $url = null, // For HTTP
public array $env = [],
public array $headers = [],
) {}
}
Security Considerations¶
Authentication Flow¶
sequenceDiagram
participant U as User
participant R as Rea
participant M as MCP Client
participant S as MCP Server
participant A as External API
U->>R: Configure integration
R->>R: Store credentials securely
U->>R: Request action
R->>M: Call tool with auth
M->>S: Request with token
S->>A: API call with credentials
A-->>S: Response
S-->>M: Tool result
M-->>R: Result
R-->>U: Display result
Security Layers¶
- Transport Security
- HTTPS for remote servers
-
Process isolation for local servers
-
Authentication
- API tokens stored in Rea's secure storage
-
Passed to servers via environment or headers
-
Authorization
- User consent for sensitive operations
- Per-server permission configuration
-
Tool-level access control
-
Input Validation
- Schema validation via JSON Schema
- Sanitization of all inputs
Performance Considerations¶
Connection Pooling¶
Maintain persistent connections to frequently-used servers:
class ConnectionPool
{
private array $connections = [];
private int $maxConnections = 10;
public function getConnection(string $serverId): MCPClient
{
if (!isset($this->connections[$serverId])) {
$this->connections[$serverId] = $this->createConnection($serverId);
}
return $this->connections[$serverId];
}
}
Caching¶
Cache tool definitions and resource metadata:
class MCPCache
{
public function cacheTools(string $serverId, array $tools, int $ttl = 300): void
{
Cache::put("mcp.tools.{$serverId}", $tools, $ttl);
}
public function getCachedTools(string $serverId): ?array
{
return Cache::get("mcp.tools.{$serverId}");
}
}
Next Steps¶
- Quick Start Guide - Get started with MCP
- PHP Client Implementation - Build the MCP client
- Rea Integration - Integrate with Rea
Architecture Decision Records
Major architectural decisions should be documented in ADRs within the Rea codebase.